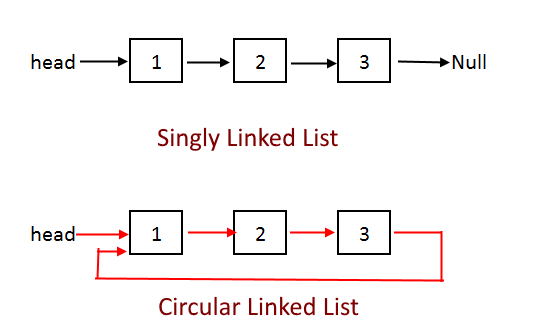
Circular Linked List is an end-connected data structure made of Nodes. Similar to the linear and doubly linked list, each node is composed of a variable data where its content is stored and a pointer to the next Node on the list.
The Linked List has a pointer to the adjacent elements but the last node is connected towards the head node i.e the first node itself, thus forming a circular shape.
- Any node can be a starting point
- Useful for implementation of queue
- Circular lists are useful in applications to repeatedly go around the list
- Circular Doubly Linked Lists are used for the implementation of advanced data structures like Fibonacci Heap.
- The size of a linked list is not fixed (dynamic size)
- Deleting and adding an element is not expensive compared to an array
- Circular lists are complex as compared to singly linked lists.
- Reversing of circular list is a complex as compared to singly or doubly lists.
- If not traversed carefully, then we could end up in an infinite loop
- Elements can be accessed sequentially not randomly compared to an array
- Extra memory allocation needs to be done for pointers which connects elements in a linked list
| Operation | Average | Worst |
|---|---|---|
| Initialize | O(1) | - |
| Access | O(n) | O(n) |
| Search | O(n) | O(n) |
| Insertion | O(1) | O(n) |
| Deletion | O(1) | O(n) |
- Allocating CPU to resources
- Multiplayer Board games
Insertion
public void insertHead(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node(data);
Node cur = head;
while(cur.getNext() != head)
cur = cur.getNext();
if(head == null)
{
head = temp;
head.setNext(head);
}
else
{
temp.setNext(head);
head = temp;
cur.setNext(temp);
}
size++;
}