|
| 1 | +# 2642. Design Graph With Shortest Path Calculator |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +- Difficulty: Hard. |
| 4 | +- Related Topics: Graph, Design, Heap (Priority Queue), Shortest Path. |
| 5 | +- Similar Questions: Number of Restricted Paths From First to Last Node, Closest Node to Path in Tree. |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +## Problem |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +There is a **directed weighted** graph that consists of `n` nodes numbered from `0` to `n - 1`. The edges of the graph are initially represented by the given array `edges` where `edges[i] = [fromi, toi, edgeCosti]` meaning that there is an edge from `fromi` to `toi` with the cost `edgeCosti`. |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +Implement the `Graph` class: |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | + |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +- `Graph(int n, int[][] edges)` initializes the object with `n` nodes and the given edges. |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +- `addEdge(int[] edge)` adds an edge to the list of edges where `edge = [from, to, edgeCost]`. It is guaranteed that there is no edge between the two nodes before adding this one. |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +- `int shortestPath(int node1, int node2)` returns the **minimum** cost of a path from `node1` to `node2`. If no path exists, return `-1`. The cost of a path is the sum of the costs of the edges in the path. |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | + |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +Example 1: |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +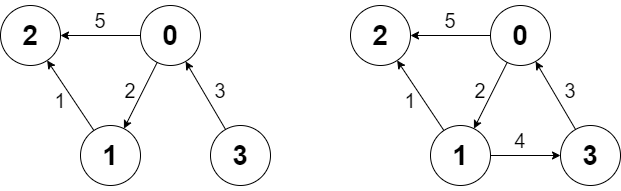 |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +``` |
| 28 | +Input |
| 29 | +["Graph", "shortestPath", "shortestPath", "addEdge", "shortestPath"] |
| 30 | +[[4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]], [3, 2], [0, 3], [[1, 3, 4]], [0, 3]] |
| 31 | +Output |
| 32 | +[null, 6, -1, null, 6] |
| 33 | +
|
| 34 | +Explanation |
| 35 | +Graph g = new Graph(4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]); |
| 36 | +g.shortestPath(3, 2); // return 6. The shortest path from 3 to 2 in the first diagram above is 3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 with a total cost of 3 + 2 + 1 = 6. |
| 37 | +g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return -1. There is no path from 0 to 3. |
| 38 | +g.addEdge([1, 3, 4]); // We add an edge from node 1 to node 3, and we get the second diagram above. |
| 39 | +g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return 6. The shortest path from 0 to 3 now is 0 -> 1 -> 3 with a total cost of 2 + 4 = 6. |
| 40 | +``` |
| 41 | + |
| 42 | + |
| 43 | +**Constraints:** |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | + |
| 46 | + |
| 47 | +- `1 <= n <= 100` |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +- `0 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1)` |
| 50 | + |
| 51 | +- `edges[i].length == edge.length == 3` |
| 52 | + |
| 53 | +- `0 <= fromi, toi, from, to, node1, node2 <= n - 1` |
| 54 | + |
| 55 | +- `1 <= edgeCosti, edgeCost <= 106` |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph at any point. |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +- At most `100` calls will be made for `addEdge`. |
| 60 | + |
| 61 | +- At most `100` calls will be made for `shortestPath`. |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | + |
| 64 | + |
| 65 | +## Solution |
| 66 | + |
| 67 | +```javascript |
| 68 | +/** |
| 69 | + * @param {number} n |
| 70 | + * @param {number[][]} edges |
| 71 | + */ |
| 72 | +var Graph = function(n, edges) { |
| 73 | + var map = Array(n).fill(0).map(() => []); |
| 74 | + for (var i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) { |
| 75 | + map[edges[i][0]].push([edges[i][1], edges[i][2]]); |
| 76 | + } |
| 77 | + this.map = map; |
| 78 | +}; |
| 79 | + |
| 80 | +/** |
| 81 | + * @param {number[]} edge |
| 82 | + * @return {void} |
| 83 | + */ |
| 84 | +Graph.prototype.addEdge = function(edge) { |
| 85 | + this.map[edge[0]].push([edge[1], edge[2]]); |
| 86 | +}; |
| 87 | + |
| 88 | +/** |
| 89 | + * @param {number} node1 |
| 90 | + * @param {number} node2 |
| 91 | + * @return {number} |
| 92 | + */ |
| 93 | +Graph.prototype.shortestPath = function(node1, node2) { |
| 94 | + var visited = {}; |
| 95 | + var queue = new MinPriorityQueue(); |
| 96 | + queue.enqueue(node1, 0); |
| 97 | + while (queue.size()) { |
| 98 | + var { element, priority } = queue.dequeue(); |
| 99 | + if (element === node2) return priority; |
| 100 | + if (visited[element]) continue; |
| 101 | + visited[element] = true; |
| 102 | + this.map[element].forEach(item => { |
| 103 | + queue.enqueue(item[0], item[1] + priority); |
| 104 | + }); |
| 105 | + } |
| 106 | + return -1; |
| 107 | +}; |
| 108 | + |
| 109 | +/** |
| 110 | + * Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such: |
| 111 | + * var obj = new Graph(n, edges) |
| 112 | + * obj.addEdge(edge) |
| 113 | + * var param_2 = obj.shortestPath(node1,node2) |
| 114 | + */ |
| 115 | +``` |
| 116 | + |
| 117 | +**Explain:** |
| 118 | + |
| 119 | +nope. |
| 120 | + |
| 121 | +**Complexity:** |
| 122 | + |
| 123 | +* Time complexity : O(n * log(m)). |
| 124 | +* Space complexity : O(n). |
0 commit comments